August 31 2020 the neck or cervical region is perhaps one of the most anatomically complex regions of the body despite being a relatively small region the contents within this region and notably the interrelationships between them hold a great deal of anatomical functional and.
Floor of carotid triangle is formed by.
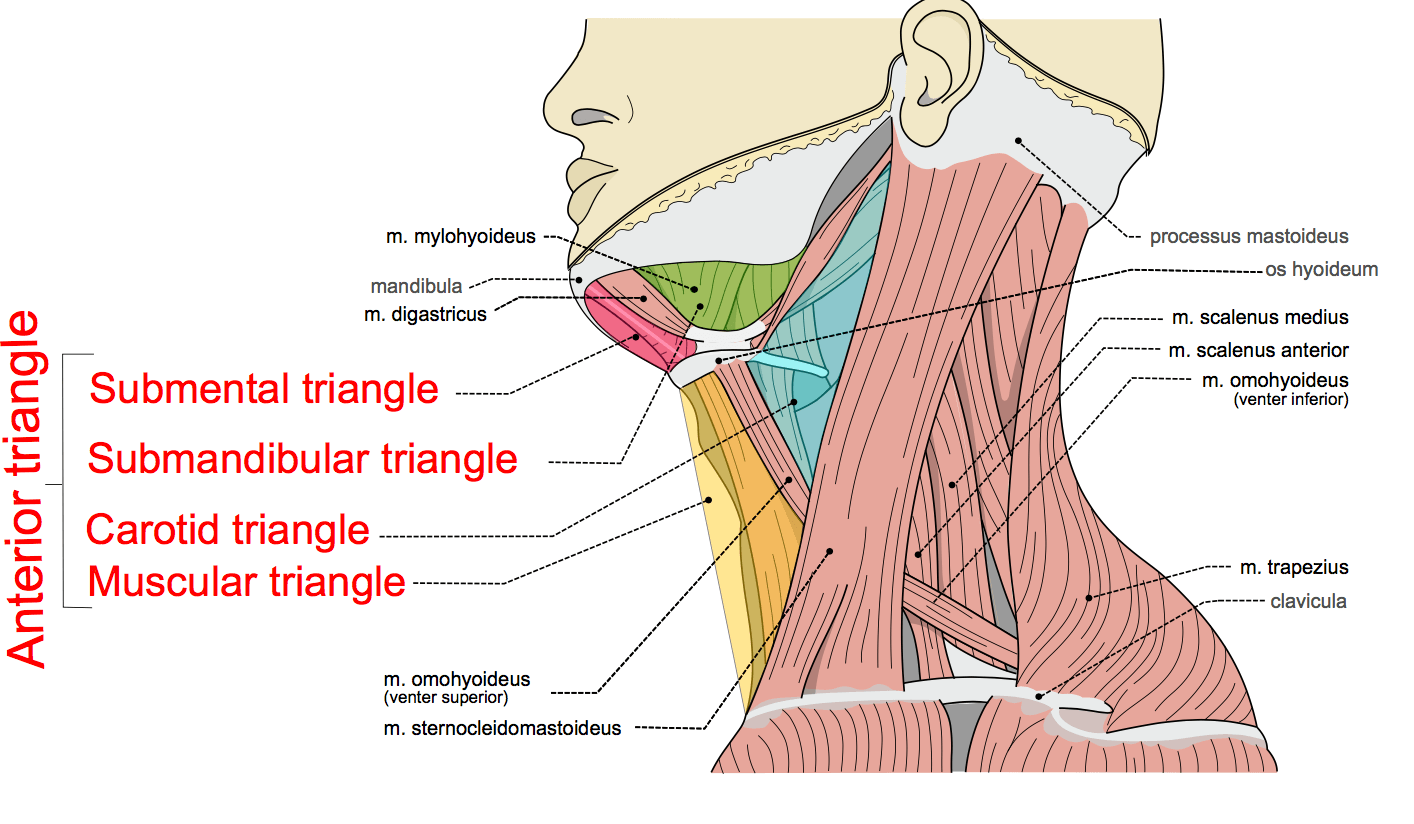
The triangles of the neck are important because of their contents as they house all the neck structures.
This muscular triangle actually has four sides and is situated more inferiorly than the other triangles.
Carotid triangle is one of the subdivisions of anterior triangle of neck.
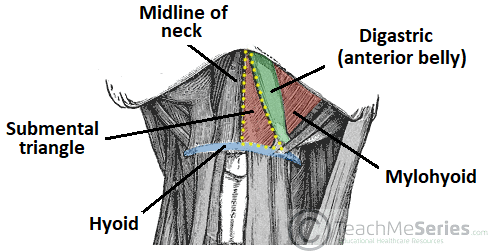
It contains the submental lymph nodes which filter lymph draining from the floor of the mouth and parts of the tongue.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle divides the neck into the two major neck triangles.
Constrictores pharyngis medius and inferior.
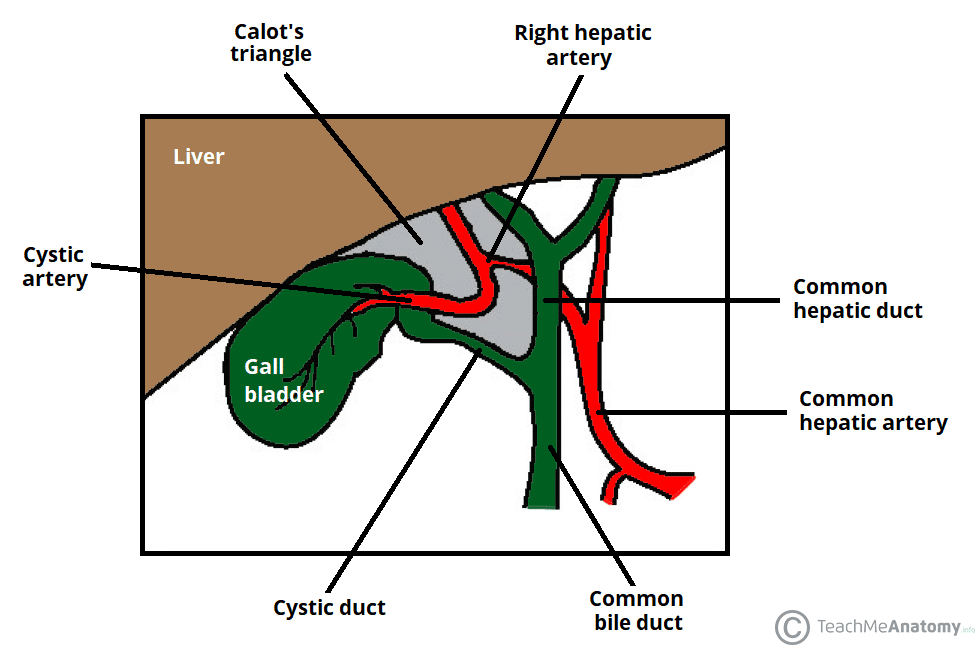
It is so called because it contains all the 3 carotid arteries viz.
The following branches of the external carotid are also met with in this space.
Common carotid artery internal jugular vein vagus nerve and hypoglossal nerve.
List the important structural contents of the carotid triangle.
Floor of digastric triangle is formed by mylohyoid anteriorly hyoglossus posteriorly infrahyoid ribbon muscles are the chief contents of muscular triangle.
The external and internal carotids lie side by side the external being the more anterior of the two.
Shahab shahid mbbs reviewer.
Uruj zehra mbbs mphil phd last reviewed.
Using the digastric and omohyoid muscles it is common to divide the anterior triangle into smaller submandibular submental carotid and muscular triangles to descriptive purposes.
Inferiorly hyoid bone.
Name the structures forming the boundaries of carotid triangle.
Hypoglossal nerve is a content of both digastric carotid triangles.
The base of the submental triangle is formed by the.
The common carotid artery bifurcates within the carotid triangle to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
Floor of the anterior cervical triangle the floor of the anterior triangle of the neck is formed mainly by the pharynx larynx and thyroid gland.
From anterior to posterior scalenus anterior scalenus medius levator scapulae splenius capitis.
The carotid triangle also contains.
Posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid.
The anterior triangle and the posterior triangle of the neck each of them containing a few subdivisions.
Its floor is formed by parts of the thyrohyoid membrane hyoglossus and the.
This triangle is situated between the ophthalmic and maxillary divisions of the trigeminal nerve and the bone of the middle fossa between the foramen rotundum and superior orbital fissure figs.
The triangles of the neck are the topographic areas of the neck bounded by the neck muscles.
This space is used to expose the superior orbital vein and the sixth cranial nerve and to access carotid cavernous fistulae.
What muscles form the floor of the posterior triangle.
Common carotid internal carotid and external carotid its boundaries are.
Superior belly of omohyoid.
Structure superficial to mylohyoid in anterior digastric triangle is mylohyoid artery nerve.